Step-by-step instructions to install & run KAPSEL †
What you need to use KAPSEL †
- Windows + Cygwin* or Linux (*Cygwin 64-bit will work fine, but if not, use Cygwin 32-bit instead.)
- gcc and make
- GOURMET (included in OCTA distribution package)
- KAPSEL source codes & examples
- kapsel3.40.zip [2018/04/01] Performance improvements by use of FFTW and memory optimization. Policy change in handling periodic boundary conditions in input.udf and restart.udf.
- kapsel3.34.zip [2018/03/06] Bug fix effective only when switch.INIT_distribution.type=user_specify
STEP 0: Linux, Windows, or Mac? †
- To build KAPSEL on Linux, goto STEP 1.
- To build KAPSEL on Windows, install "Cygwin" first, then goto STEP 1. Be sure to include "gcc", "make" (both exist under "Devel" tree) and libfftw3-devel (under "Math" tree). Both 32-bit and 64-bit cygwin should work fine.
- KAPSEL can be build also on Mac OS-X (not officially supported). By default, gcc command calls clang compiler which is not fast. You may install gcc and fftw separately by yourself to achieve better performance.
STEP 1: Download and install OCTA/GOURMET †
- Visit OCTA-BBS and Download an appropriate version of KAPSEL installation package.
Please contact us [kapsel.dev@gmail.com] if any troubles take place.
- In the following STEPS, OCTA8.# is assumed to be installed in /usr/local/OCTA8# (Linux/Mac) or C:\OCTA8.# (Windows).
STEP 2: Build "libplatform" †
- "libplatform" is an I/O library developed by OCTA project. One needs this library to access to UDF-formatted files.
- You may have to install additional software such as Java(JDK) and Python3 to build libplatform.
> su
> cd /usr/local/OCTA8#/GOURMET/src
> make clean
> ./configure
> make
> make install
- For Windows:
- Logon Windows with an administrator authorization
- Open Cygwin terminal window
$ ln -s /cygdrive/c/OCTA8.# /usr/local/OCTA8#
$ cd /usr/local/OCTA8#/GOURMET/src
$ make clean
$ ./configure
$ make (in case of error, make CCOPT=)
$ make install
- In my environment, I had to do the following before "./configure".
> touch aclocal.m4
> touch config.h.in
> touch Makefile.in
> touch configure
> cd /usr/local/OCTA8#/GOURMET/src
> make distclean; make clean
> ./configure CC=gcc-7 CXX=g++-7
> make
> sudo make install
> mv ../lib/macosx/libplatform.a ../lib/macosx/libplatform_gcc-7.a
> ./configure CC=clang CXX=clang++
- In my environment, gourmet doesn't start properly after building libplatform. Please do the following if so.
> cd ..
> Make-All.sh
- See manuals for more detailed information on libplatform
STEP 3: Download "KAPSEL" source code †
- You can download KAPSEL source codes & examples at the top of this page.
STEP 4: Build "KAPSEL" binary executable †
> unzip kapsel3.*.zip
> cd kapsel3.*
- You may modify GOURMET_HOME_PATH in the attached "Makefile" so that the library "libplatform.a" is correctly linked.
- "*" indicates the performance.
- Clean-up working files first.
> make clean
- with Ooura FFT (easy to build but slow, not compatible with OpenMP)
> make ENV=CYGWIN (Cygwin on Windows)*
or
> make ENV=GCC (gcc on Linux)*
or
> make ENV=ICC (icc on Linux)*
or
> make ENV=GCC_MAC (gcc on Mac)*
or
> make ENV=CLANG (clang on Mac)
- with Intel MKL (as fast as FFTW, compatible with OpenMP)
> make ENV=ICC FFT=IMKL (icc on Linux)**
or
> make ENV=ICC_OMP FFT=IMKL (icc on Linux, OpenMP)***
- with FFTW (faster than Ooura, compatible with OpenMP)
> make ENV=CYGWIN FFT=FFTW (Cygwin on Windows)**
or
> make ENV=CYGWIN_OMP FFT=FFTW (Cygwin on Windows, OpenMP)***
or
> make ENV=GCC FFT=FFTW (gcc on Linux)**
or
> make ENV=GCC_OMP FFT=FFTW (gcc on Linux, OpenMP)***
or
> make ENV=ICC FFT=FFTW (icc on Linux)**
or
> make ENV=ICC_OMP FFT=FFTW (icc on Linux, OpenMP)****
or
> make ENV=GCC_MAC FFT=FFTW (gcc-7 on Mac)**
or
> make ENV=GCC_MAC_OMP FFT=FFTW (gcc-7 on Mac, OpenMP)***
- Installation memo of FFTW
- For Windows
- Install "libfftw3-devel" using Cygwin installer.
- For Linux
- Download source file and
- with gcc
./configure CFLAGS="-O3" FFLAGS="-O3" --enable-openmp --enable-threads --enable-shared --disable-fortran
make
make install
./configure --prefix=/opt/fftw/3.3.7 CC=icc CXX=icpc CFLAGS="-O3" FFLAGS="-O3" --enable-openmp --enable-threads --enable-shared --disable-fortran --enable-sse2 --enable-avx --enable-avx2
make
make install
./configure --prefix=/opt/fftw/3.3.7 CC=gcc-7 CXX=g++-7 CFLAGS="-O3" FFLAGS="-O3" --enable-openmp --enable-threads --enable-shared --disable-fortran
make
sudo make install
STEP 5: Test run †
> cd UDF
> ../kapsel -Iinput.udf -Ooutput.udf -Ddefine.udf -Rrestart.udf
#using input.udf as input
#using output.udf as output
#using define.udf as definition
#using restart.udf as restart
...
#output.udf end.
#restart.udf end.
#Simulation has ended!
#Total Running Time (s): 24.77
# (m): 0.41
# (h): 0.01
#Average Step Time (s): 0.02
# (m): 0.00
# (h): 0.00
- If you see a command-line output as shown above, KAPSEL has been successfully built and run.
STEP 6: Visualization of simulation data †
- The sample input.udf conduct a simulation of sedimenting 5-heavier + 5-lighter particles in Newtonian fluid, which is resolved by a 32x32x32 CFD grids. It takes less than a minute to be completed. If this sample successfully run, "output.udf" will be created. You can visualize various simulation data using python script from Gourmet. Three simple examples are shown below.
- Common procedure
- Start GOURMET
- Open "output.udf" ("File" -> "Open" -> Open "output.udf").
- Watching variables on Gourmet
- Instantaneous positions and velocities of all the particles can be seen as variables in "Particles[]". Use slide bar at the bottom of GOURMET viewer window to see variables at different time steps.
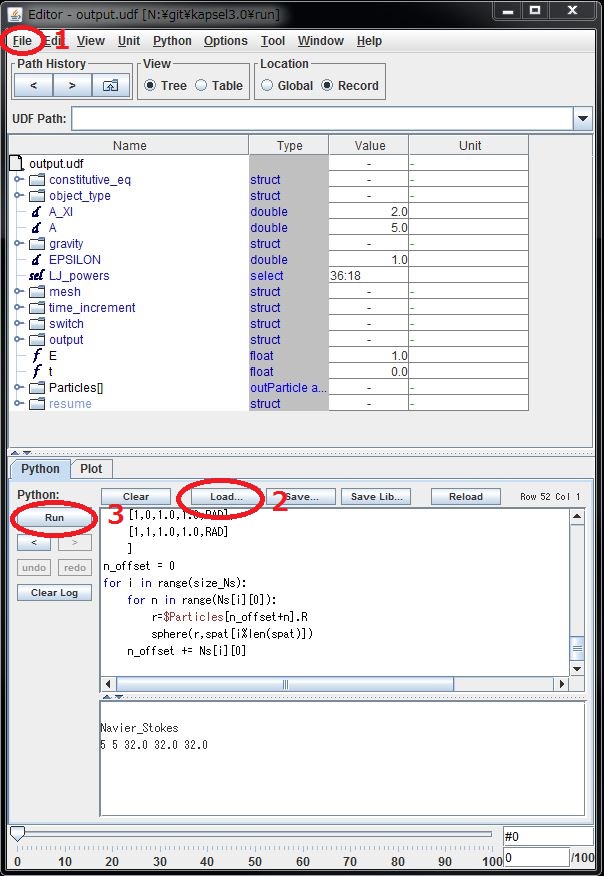
- Making an animation on GOURMET
- Go down to "Python" panel, and click "Load"
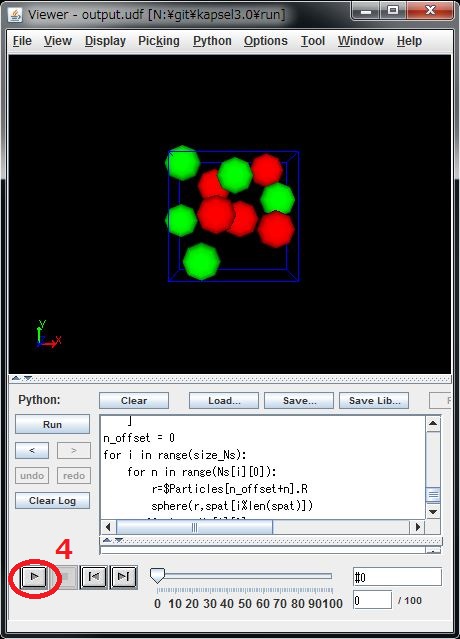
- Open "particleshow.py", and click "Run"
- A new window will open, then click the playback button there.
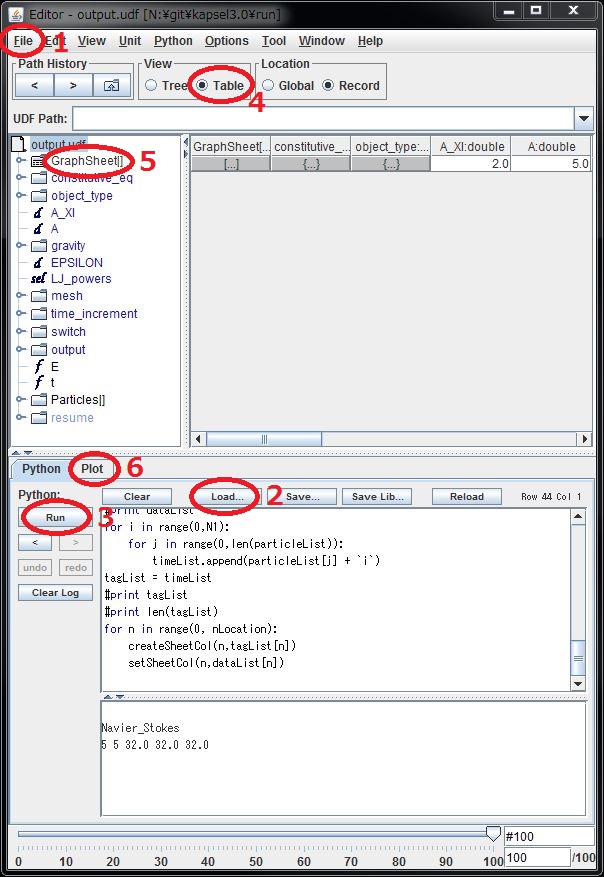
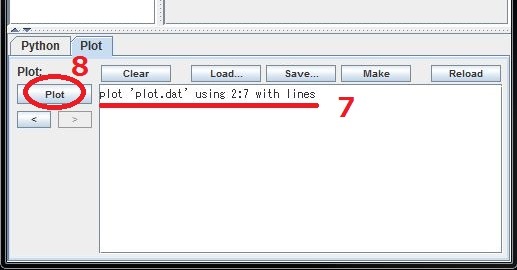
STEP 7: Analyzing simulation data †
- The history of simulation run (instantaneous positions and velocities of particles) is stored in "output.udf". One can access to this file by one of the following methods.
- Python program. Please read the manual below for more general information on accessing UDF using Python.
- Fortran or C program with libplatform. Please read the manual below more general information on accessing UDF using Fortran or C.
- KAPSEL returns several important data to stderr as well (temporal stress etc). It usually appears in command line, but one can redirect stderr to a file as follows.
 libplatform_eng.pdf
libplatform_eng.pdf libplatform_jpn.pdf
libplatform_jpn.pdf pythoninterface_eng.pdf
pythoninterface_eng.pdf PythonInterface_jpn.pdf
PythonInterface_jpn.pdf libplatform_eng.pdf
libplatform_eng.pdf libplatform_jpn.pdf
libplatform_jpn.pdf




